本文将介绍如何使用Cassandra数据库来构建.NET应用。这里,我们将进行一个简单的收益计算,我们将使用使用2个交易系统——Debit、Credit,以及2个参考系统——Customer、ForexRate。

传统做法
对于给定的问题,应用程序将使用的关系型数据存储来开发。关系数据库模型是由Edgar F. Codd在1969年末首先提出的。关系数据模型的基本假设是数据可以数学的表示为一个1对n的关系,即可以认为是笛卡尔积的子集。数据可以通过使用集合理论访问,一致性可以通过应用主键和外键关系约束的代数访问方法来实现。
在当今的数据世界中,传统的数据存储方法更不上工业数据增长的规模。
目标状态
这正是本文将讨论的,如何使用大数据Cassandra后端而不是使用传统方案来构建.NET应用。针对这一问题,本文将着手从架构设计一直到.NET的实现代码。
架构
基础设施
因为分布在一个三层架构中,基础设施包含展示,业务和存储(Cassandra)层。具有高度可用的对等集群模型的优点,Cassandra层用两个节点集群构建。
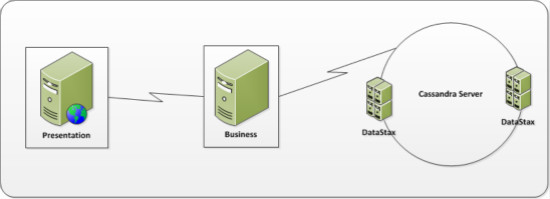
业务和存储层使用被称为CassandraSharp的大数据Cassandra连接器连接。你可以通过GitHub的项目了解更多的关于CassandraSharp的信息。
逻辑
逻辑架构定义了提供给业务需求的活动和功能的流程。逻辑架构是独立于技术和实现的。
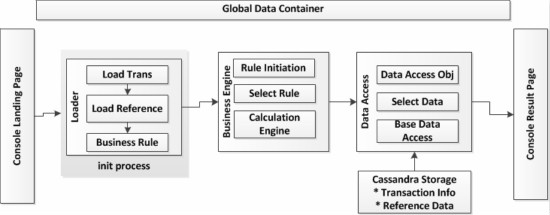
在我们的任务中,我们的功能被细分为六大类。控制台登录(Console Landing)是输入层,控制台结果(Console Result)是输出层。全局数据容器(Global data container)是贯穿整个应用的数据持有者。关键功能包含了剩下的三个区域:加载器(Loader),业务引擎(BusinessEngine)和数据访问(DataAccess)。
加载器模块在流程初始化(AppInit)期间加载业务,参考和业务规则。业务引擎根据输入在业务层选择计算的规则。数据访问位于数据连接层用于读取和存储Cassandra中的信息。
数据
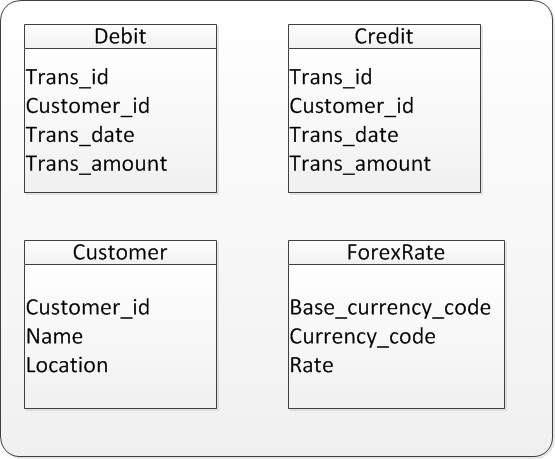
给定的问题描述,处理两个事物数据和两个引用数据。他们分别被标记为 Debit,Credit ,Customer,ForexRate。如下图所示:
实现
给定的问题描述,我们覆盖了目标和基础设施、逻辑和数据架构。让我们用.NET编程并用Cassandra作为数据存储来实现这个需求。
Cassandra查询
由于我们将 Cassandra作为存储, Cassandra表(列族)按照我们的数据模型在后台被创建。实际的创建 Cassandra表(列族)的CQL( Cassandra查询语言)如下:
CREATE TABLE Debit (
Trans_id int PRIMARY KEY,
Customer_id int,
Trans_amount varchar,
Trans_date varchar
)
CREATE TABLE Customer (
Customer_id int PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar,
Location varchar
)
Cassandra连接器
我们知道 ADO.NET通过 SQL Server 和 XML提供数据持久化服务, 并通过 OLE DB 和 ODBC来操作数据. 所以, ADO.NET将数据操作分片划分. ADO.NET 包括.NET 框架数据提供连接数据库,执行命令以及获取数据的操作.
类似的 Cassandra也可以通过 CassandraSharp连接. 这是Apache Cassandra 一个高性能 .NET 驱动. 在CassandraSharp命名空间里有 ClusterManager, TransportConfig, ClusterConfig, BehaviourConfig, 等等. 可以从Github https://github.com/pchalamet/cassandra-sharp 查看
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data;
using Apache.Cassandra;
using CassandraSharp;
using CassandraSharp.Config;
namespace DataAccess
{
publicabstract class BaseDataAccess : IDisposable
{
pri ate string[] myClusters;
private int myPort;
public BaseDataAccess(string[] clusters,int port)
{
myClusters = clusters;
myPort = port;
}
protected ICluster GetCluster()
{
CassandraSharpConfig config = new CassandraSharpConfig();
ClusterConfig clusterConfig = new ClusterConfig();
TransportConfig transConfig = new TransportConfig();
clusterConfig.Name = "TestCassandra";
transConfig.Port = myPort;
clusterConfig.Transport = new TransportConfig();
EndpointsConfig endPointConfig = new EndpointsConfig();
endPointConfig.Servers = myClusters;
endPointConfig.Snitch = SnitchType.Simple;
endPointConfig.Strategy = EndpointStrategy.Nearest;
BehaviorConfig behaveConfig = new BehaviorConfig();
behaveConfig.KeySpace = ConfigEntries.DefaultDatabase;
if (!String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ConfigEntries.UserName)) behaveConfig.User= ConfigEntries.UserName;
if (!String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(ConfigEntries.Password)) behaveConfig.Password= ConfigEntries.Password;
behaveConfig.ReadConsistencyLevel = Apache.Cassandra.ConsistencyLevel.ONE;
behaveConfig.WriteConsistencyLevel = Apache.Cassandra.ConsistencyLevel.ONE;
clusterConfig.Transport = transConfig;
clusterConfig.Endpoints = endPointConfig;
clusterConfig.BehaviorConfig = behaveConfig;
config.Clusters = new ClusterConfig[] { clusterConfig };
//We need to ensure that the connection is not initialized before configuring...
ClusterManager.Shutdown();
ClusterManager.Configure(config);
ICluster cluster = ClusterManager.GetCluster("TestCassandra");
return cluster;
}
protected DataTable ConvertCqlResultToDataTable(CqlResult result, stringtableName)
{
DataCommon common = new DataCommon();
DataTable store = common.GetSchema(result, tableName);
return PopulateData(result, common, store);
}
private DataTable PopulateData(CqlResult result, DataCommon common, DataTablestore)
{
string columnName = string.Empty;
foreach (CqlRow row in result.Rows)
{
DataRow dataRow = store.NewRow();
foreach (Column column in row.Columns)
{
columnName = common.GetValue<string>(column.Name);
dataRow[columnName] = common.GetValue(store.Columns[columnName],column.Value);
}
store.Rows.Add(dataRow);
}
return store;
}
public void Dispose()
{
ClusterManager.Shutdown();
}
}
}
在DataAccess 对象里, GetCluster方法从配置文件获取Cassandra cluster . 其包含了Cluster的各种详细信息,比如服务器地址, 用户名密码, 持久化级别, Endpoint 策略, 等.
我们需要泛型方法来从Cassandra 指定的 DataTable得到数据. ConvertCqlResultToDataTable方法就是实现了这一需求.
PopulateData 是前一个方法的内部方法. PopulateData通过meta data读取 Cassandra Table表的数据; 将结果返回为 DataTable 型.
数据类型访问
.NET框架和Cassandra 在存储数据格式上各有不同. 下面讲讲他们的同步. Cassandra 通过列表式标书数据,其属性如下:
| Property | Type |
| Name | CompareWith type |
| Value | binary |
| Timestamp | 64-bit integer |
CompareWith配置在文件里可以置为 ASCII, UTF8, LexicalUUID, TimeUUID, Long, or Bytes.也就是说在 .NET 环境里可以是 string, Guid, DateTime, long, or byte[]. 数值只能是Bytes 或byte[] . Timestamp是用来同步 Cassandra 服务器的,一般不能改动. 下面展示了列数据设置保存后value属性的情况.
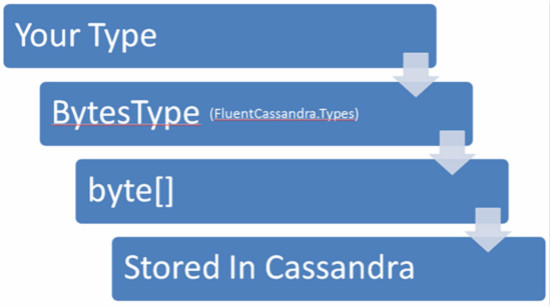
当保存 Cassandra的相关属性值时,一般是这样两步执行的。 首先序列化目标类型然放于 Cassandra’s 的BytesType,并自动保证其运行态的正确转换. 这种模式也是 ASCII, UTF8, LexicalUUID, TimeUUID, Long, and Bytes序列化其列名的主要驱动.
按上述方法,DataCommon就可以处理 .NET and Cassandra 之间的各种数据类型了
namespace DataAccess
{
internalclass DataCommon
{
internal DataTable GetSchema(CqlResult result, string tableName)
{
if (result != null && result.Type == CqlResultType.ROWS)
{
return BuildTable(result.Schema,tableName);
}
else throw new ArgumentNullException("result", "'result'parameter must not be empty and it should contain atleast one row");
}
internal DateTime GetDate(byte[] value)
{
if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian) Array.Reverse(value);
return GetDateTimeFromLong(BitConverter.ToInt64(value, 0));
}
internal string GetName(byte[] value)
{
return GetValue<string>(value);
}
static IDictionary<string,>> dataProcessors;
private IDictionary<string,>> GetDataProcessors()
{
if (dataProcessors == null)
{
//TODO: More data type processorsneeds to be added.
dataProcessors = new Dictionary<string,>>();
dataProcessors["string"]= (byteValue) => GetValue<string>(byteValue);
dataProcessors["decimal"]= (byteValue) => GetIntValue(byteValue);
dataProcessors["double"]= (byteValue) => GetValue(byteValue);
dataProcessors["bool"]= (byteValue) => GetValue<bool>(byteValue);
dataProcessors["int"]= (byteValue) => GetIntValue(byteValue);
dataProcessors["long"]= (byteValue) => GetValue<long>(byteValue);
dataProcessors["datetime"]= (byteValue) => GetDate(byteValue);
}
return dataProcessors;
}
internal object GetValue(DataColumn column, byte[] value)
{
return GetDataProcessors()[column.DataType.Name.ToLower()](value);
}
internal decimal GetDecimalValue(byte[] value)
{
//check that it is even possible to convert the array
if (value.Count() != 16)
throw new Exception("A decimalmust be created from exactly 16 bytes");
//make an array to convert back toint32
Int32[] bits = new Int32[4];
for (int i = 0; i <= 15; i += 4)
{
//convert every 4 bytes into anint32
bits[i / 4] = BitConverter.ToInt32(value,i);
}
return new decimal(bits);
}
internal double GetValue(byte[] value)
{
if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian)
Array.Reverse(value); //need thebytes in the reverse order
return BitConverter.ToDouble(value, 0);
}
internal int GetIntValue(byte[] value)
{
if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian)
Array.Reverse(value); //need thebytes in the reverse order
return BitConverter.ToInt32(value, 0);
}
internal T GetValue<t>(byte[] value)
{
return (T)Convert.ChangeType(Encoding.Default.GetString(value), typeof(T));
}
internal long GetDateTimeInLong(DateTime value)
{
DateTime Epoch = new DateTime(1970, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, DateTimeKind.Utc);
TimeSpan elapsedTime = value - Epoch;
return (long)elapsedTime.TotalSeconds;
}
internal DateTime GetDateTimeFromLong(long value)
{
return new DateTime(1970, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, DateTimeKind.Utc).AddSeconds(Math.Round(value* 1.0));
}
private DataTable BuildTable(CqlMetadata metadata, string tableName)
{
DataTable dataStore = new DataTable();
foreach (KeyValuePair<byte[],> column in metadata.Value_types)
{
DataColumn dataColumn = new DataColumn();
dataColumn.ColumnName = GetValue<string>(column.Key);
dataColumn.DataType = GetColumnType(column.Value);
dataStore.Columns.Add(dataColumn);
}
return dataStore;
}
static IDictionary<string,> typeProvider;
private IDictionary<string,> GetCqlToDotNetTypeProviders()
{
if (typeProvider == null)
{
typeProvider = new Dictionary<string,>();
typeProvider["AsciiType"]= typeof(string);
typeProvider["BytesType"]= typeof(byte[]);
typeProvider["BooleanType"]= typeof(bool);
typeProvider["CounterColumnType"]= typeof(int);
typeProvider["DateType"]= typeof(DateTime);
typeProvider["DecimalType"]= typeof(decimal);
typeProvider["DoubleType"]= typeof(double);
typeProvider["DynamicCompositeType"]= typeof(string);
typeProvider["FloatType"]= typeof(decimal);
typeProvider["IntegerType"]= typeof(int);
typeProvider["LexicalUUIDType"]= typeof(Guid);
typeProvider["LongType"]= typeof(long);
typeProvider["TimeUUIDType"]= typeof(DateTime);
typeProvider["UTF8Type"]= typeof(string);
typeProvider["UUIDType"]= typeof(Guid);
}
return typeProvider;
}
private Type GetColumnType(string cqlType)
{
return GetCqlToDotNetTypeProviders()[cqlType];
}
}
}
强制转换BytesType 保证了 .NET在反序列化时不会出错. 这需要一些小技巧,但最终结果是一致的. 你向数据库里插入了希望保存的数据类型。
Data Access Object
业务层设计, DAO (Data Access Object) 是关键所在. 2个交易和两个数据映射的开发模式如下:
namespace DataAccess
{
publicclass CreditDAO : BaseDataAccess, ISelectAllData, ISelectData
{
public CreditDAO()
: base(ConfigEntries.Clusters, ConfigEntries.Port)
{ }
DataTable ISelectData.GetSpecificData(string query, object[] parameters)
{
CqlResult result = base.GetCluster().ExecuteCql(string.Format(query, parameters));
return ConvertCqlResultToDataTable(result, "Credit");
}
DataTable ISelectAllData.GetData()
{
CqlResult result = base.GetCluster().ExecuteCql(DbConstants.SelectCreditData);
return ConvertCqlResultToDataTable(result, "Credit");
}
}
}
DAO 通过BaseDataAccess 对象完成扩展. SelectData接口通过给定参数获取相应数据. 因此SelectAllData接口为指定的 DAO捕获数据.
Data Common
ConfigEntries对象是在Common命名空间下完成全局配置属性的. ConfigEntries 类具备集群服务器的通用属性, 比如端口, 数据库, 用户名密码.
namespace Common
{
publicclass ConfigEntries
{
public static string[] Clusters = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["Clusters"].Split(newstring[] { "|" }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
public static int Port = Convert.ToInt32(ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["Port"]);
public static string DefaultDatabase = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["DefaultDatabase"];
public static string UserName = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["UserName"];
public static string Password = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["Password"];
}
}
写这些模板代码的用意就是针对特定的架构设计实现特定的功能. 最终实现基于Dotnet Cassandra存储的应用开发.
代码下载地址:http://www.codeproject.com/KB/NoSQL/758803/CodeBase.zip
我们一直都在努力坚持原创.......请不要一声不吭,就悄悄拿走。
我原创,你原创,我们的内容世界才会更加精彩!
【所有原创内容版权均属TechTarget,欢迎大家转发分享。但未经授权,严禁任何媒体(平面媒体、网络媒体、自媒体等)以及微信公众号复制、转载、摘编或以其他方式进行使用。】
微信公众号
TechTarget
官方微博
TechTarget中国
相关推荐
-
MongoDB与Cassandra数据库对比
MongoDB和Cassandra都属于NoSQL数据库系列,它们也恰好都是开源,但是,它们的相似之处仅此而已 […]
-
如何玩转NoSQL数据库?CIO亲身体验MongoDB,Riak和Cassandra
Weather公司CIO Bryson Koehler整理出了MongoDB,Riak和Cassandra等NoSQL数据库的特性。他指出这其中最重要的特性是“NoSQL不会限制住你”。
-
2014年11月数据库流行度排行榜 几家欢喜几家愁
本月榜单中,前十名从名次上看,仅有的变化在于第九名Cassandra和第十名Sybase ASE的名次对调。
-
2014年9月数据库流行度排行榜
在关系型数据库前五名中,开源数据库 MySQL 和PostgreSQL 的积分都有所上升,商业数据库 Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server 和 DB2的积分都在下降。
