本文针对诸如select top n 这类返回一定数量记录的查询操作,来分析mongodb是如何将查询结果装填到结果集中的。这里要说明的是之前文章中的大部分程序流程,在select top 这类操作也都是要执行的,所以这里接着之前文章所说的内容,继续向底层挖掘相应的功能逻辑。
之前查询流程中介绍过QueryPlanSet::Runner::run()方法,它本身为struct类型,主要是用于对执行步骤进行封装(形成依次执行的操作流),如下(详情见注释):
| //queryoptimizer.cpp shared_ptr< QueryOp > QueryPlanSet::Runner::run() { …… //遍历查询操作集合,找到已执行完成的操作 for( vector< shared_ptr< QueryOp > >::iterator i = ops.begin(); i != ops.end(); ++i ) { initOp( **i ); if ( (*i)->complete() ) return *i; } //将查询操作集合转换成查询队列 std::priority_queue< OpHolder > queue; for( vector< shared_ptr< QueryOp > >::iterator i = ops.begin(); i != ops.end(); ++i ) { if ( !(*i)->error() ) { queue.push( *i ); } } while( !queue.empty() ) { mayYield( ops ); //找出队首的查询操作 OpHolder holder = queue.top(); queue.pop(); QueryOp &op = *holder._op; //执行下一操作,如果是userqueryop类型,则会执行query.cpp中的next()方法(位于734行) //该方法会最终将查询结果绑定到response message中(注:通过调用finish方法) nextOp( op ); if ( op.complete() ) {//如执行完成 if ( _plans._mayRecordPlan && op.mayRecordPlan() ) { op.qp().registerSelf( op.nscanned() ); } return holder._op; } if ( op.error() ) { continue; } queue.push( holder );//如未执行完成,再次该查询操作入队(尾) //使用查询计划? if ( !_plans._bestGuessOnly && _plans._usingPrerecordedPlan && op.nscanned() > _plans._oldNScanned * 10 && _plans._special.empty() ) { holder._offset = -opnscanned(); _plans.addOtherPlans( true ); PlanSet::iterator i = _plans._plans.begin(); ++i; for( ; i != _plans._plans.end(); ++i ) { shared_ptr< QueryOp > op( _op.createChild() ); op->setQueryPlan( i->get() ); ops.push_back( op ); initOp( *op ); if ( op->complete() ) return op; queue.push( op ); } _plans._mayRecordPlan = true; _plans._usingPrerecordedPlan = false; } } return ops[ 0 ]; } void QueryPlanSet::Runner::nextOp( QueryOp &op ) { GUARD_OP_EXCEPTION( op, if ( !op.error() ) { op.next(); } ); } |
因为UserQueryOp是QueryOp的子类,如下图:
因为本文是UserQueryOp对象,则上面代码段中的nextOp()会最终调用该对象的next方法:
//query.cpp
virtual void next() {
…..
if ( !_c || !_c->ok() ) {
finish( false );
return;
}
bool mayCreateCursor1 = _pq.wantMore() && ! _inMemSort && _pq.getNumToReturn() != 1 && useCursors;
if( 0 ) {
cout << “SCANNING this: ” << this << ” key: ” << _c->currKey() << ” obj: ” << _c->current() << endl;
}
//判断是否超出扫描项限制,形如:db.foo.find()._addSpecial( “$maxScan” , 50 )
if ( _pq.getMaxScan() && _nscanned >= _pq.getMaxScan() ) {
finish( true ); //直接返回
return;
}
_nscanned = _c->nscanned();
if ( !matcher()->matches(_c->currKey(), _c->currLoc() , &_details ) ) {
//未匹配,则指向下一条记录
if ( _details.loadedObject )
_nscannedObjects++;//扫描对象累加1
}
else {
_nscannedObjects++;//扫描对象累加1
DiskLoc cl = _c->currLoc();
//当前是否使用shard分片,且是否在当前shard chunk中
if ( _chunkManager && ! _chunkManager->belongsToMe( cl.obj() ) ) {
_nChunkSkips++;
// log() << “TEMP skipping un-owned chunk: ” << _c->current() << endl;
}
else if( _c->getsetdup(cl) ) {//值是否重复
// dup
}
else {
//如匹配
if ( _inMemSort ) {//当使用scanAndOrder
// note: no cursors for non-indexed, ordered results. results must be fairly small.
_so->add( _pq.returnKey() ? _c->currKey() : _c->current(), _pq.showDiskLoc() ? &cl : 0 );
}
else if ( _ntoskip > 0 ) {
_ntoskip–;
}
else {
if ( _pq.isExplain() ) {//如果使用explain指令(用于显示如何执行当前指令)
_n++;
if ( n() >= _pq.getNumToReturn() && !_pq.wantMore() ) {
// .limit() was used, show just that much.
finish( true );
return;
}
}
else {
if ( _pq.returnKey() ) {
BSONObjBuilder bb( _buf );
bb.appendKeys( _c->indexKeyPattern() , _c->currKey() );
bb.done();
}
else if ( _keyFieldsOnly ) {
fillQueryResultFromObj( _buf , 0 , _keyFieldsOnly->hydrate( _c->currKey() ) );
}
else {
BSONObj js = _c->current();
assert( js.isValid() );
if ( _oplogReplay ) {
BSONElement e = js[“ts”];
if ( e.type() == Date || e.type() == Timestamp )
_slaveReadTill = e._opTime();
}
//将当前记录填充到_buf中,以便finish方法使用该对象
fillQueryResultFromObj( _buf , _pq.getFields() , js , (_pq.showDiskLoc() ? &cl : 0));
}
_n++;
if ( ! _c->supportGetMore() ) {
if ( _pq.enough( n() ) || _buf.len() >= MaxBytesToReturnToClientAtOnce ) {
finish( true );
return;
}
}
//判断是否已够返回一批数据
else if ( _pq.enoughForFirstBatch( n() , _buf.len() ) ) {
/* if only 1 requested, no cursor saved for efficiency…we assume it is findOne() */
if ( mayCreateCursor1 ) {
_wouldSaveClientCursor = true;
if ( _c->advance() ) {
// more…so save a cursor
_saveClientCursor = true;
}
}
//查询结束,绑定查询结果数据到response
finish( true );
return;
}
}
}
}
}
//将游标指向下一条记录,该方法参见
//http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/04/15/mongodb_cursor_source_code.html
_c->advance();
}
上面代码是实现了对相应cursor的遍历查询,找出(matches)合适的数据,并最后将结果添加到_buf对象中,之后再使用finish方法将_buf绑定到response中(向client发送信息),如下:
// query.cpp
// this plan won, so set data for response broadly
void finish( bool stop ) {
if ( _pq.isExplain() ) {
_n = _inMemSort ? _so->size() : _n;
}
//当使用scanAndOrder(位于scanandorder.h),表示索引不能用于排序(sort)
else if ( _inMemSort ) {
if( _so.get() )
_so->fill( _buf, _pq.getFields() , _n );
}
if ( _c.get() ) {
_nscanned = _c->nscanned();
//tailable设置
if ( _pq.hasOption( QueryOption_CursorTailable ) && _pq.getNumToReturn() != 1 )
_c->setTailable();
// If the tailing request succeeded.
if ( _c->tailable() )
_saveClientCursor = true;//是否保存ClientCursor
}
if ( _pq.isExplain() ) {
massert( 13638, “client cursor dropped during explain query yield”, _c.get() );
_eb.noteScan( _c.get(), _nscanned, _nscannedObjects, _n, scanAndOrderRequired(),
_curop.elapsedMillis(), useHints && !_pq.getHint().eoo(), _nYields ,
_nChunkSkips, _keyFieldsOnly.get() > 0 );
}
else {
if ( _buf.len() ) {
//将_buf绑定到_response
_response.appendData( _buf.buf(), _buf.len() );
_buf.decouple();
}
}
if ( stop ) {
setStop();/*设置完成标志位”_complete”和_stopRequested
(用于MultiPlanScanner::runOp判断条件)*/
}
else {//设置完成标志位”_complete”
setComplete();
}
}
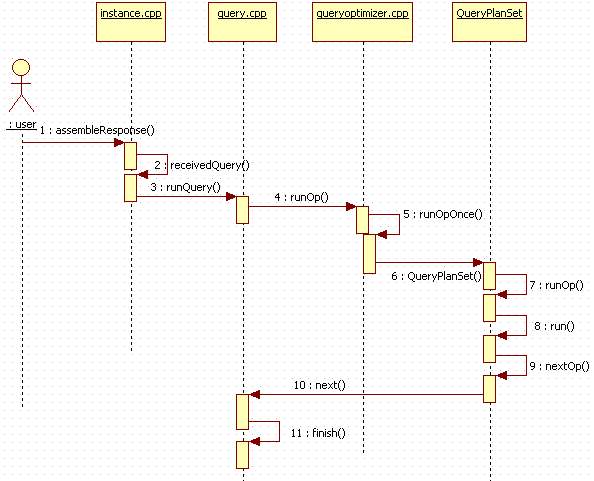
好了,今天的内容到这里就告一段落了,最后用一张时序图来总结一下查询(select top)在mongodb中的执行流程:
我们一直都在努力坚持原创.......请不要一声不吭,就悄悄拿走。
我原创,你原创,我们的内容世界才会更加精彩!
【所有原创内容版权均属TechTarget,欢迎大家转发分享。但未经授权,严禁任何媒体(平面媒体、网络媒体、自媒体等)以及微信公众号复制、转载、摘编或以其他方式进行使用。】
微信公众号
TechTarget
官方微博
TechTarget中国
相关推荐
-
MongoDB与Cassandra数据库对比
MongoDB和Cassandra都属于NoSQL数据库系列,它们也恰好都是开源,但是,它们的相似之处仅此而已 […]
-
OpenWorld18大会:Ellison宣布数据库的搜寻和破坏任务
在旧金山举行的甲骨文OpenWorld 2018大会中,甲骨文首席技术官(CTO)兼创始人Larry Elli […]
-
eHarmony公司利用Redis NoSQL数据库进行热存储
虽然关系型数据库不会消失,但关系型数据库管理系统有时仅在会话管理、推荐引擎和模式匹配等关键Web应用程序中担当 […]
-
ObjectRocket着力发展Azure MongoDB服务
MongoDB吸引了微软公司的注意力,微软公司计划针对运行于该公司2017年发布的Azure Cosmos D […]
