首先我们看一下Balancer及相关实现策略的类图:

可以看到Balancer类里包含一个BalancerPolicy,其指向一个均衡策略,该策略会实现查找并收集要迁移的chunk。
这里先看一下Balancer的类定义,如下:
| //balace.h class Balancer : public BackgroundJob { public: Balancer(); virtual ~Balancer(); // BackgroundJob methods virtual void run(); virtual string name() const { return “Balancer”; } private: typedef BalancerPolicy::ChunkInfo CandidateChunk; typedef shared_ptr CandidateChunkPtr; //mongos名称(hostname:port) string _myid; // Balancer 启动时间 time_t _started; // 前移的chunks数量 int _balancedLastTime; // 均衡策略(确定要迁移的chunks) BalancerPolicy* _policy; //初始化,检查balancer 能否链接到servers.该方法可能抛出网络异常 bool _init(); /** * 收集关于shards及chunks的信息,以及可能需要迁移的chunks * @param conn: 指向config server(s)连接 * @param candidateChunks (IN/OUT): 可能需要迁移的chunks */ void _doBalanceRound( DBClientBase& conn, vector* candidateChunks ); /** * 逐个迁移chunk.并返回最终迁移的chunk数量 * @param candidateChunks 可能需要迁移的chunks * @return number of chunks effectively moved */ int _moveChunks( const vector* candidateChunks ); /*在config server(s)中标记并前balancer为活动状态.*/ void _ping( DBClientBase& conn ); //当configdb中的所有服务均可用时,返回true bool _checkOIDs(); }; |
可以看出balancer继承自BackgroundJob,所以它是以后台方式运行的。了解了该类的方法和属性之后,下面我们着手看一下mongos主函数中启动balancer.go()的调用流程。因为balancer继承自BackgroundJob,所以还要看一下BackgroundJob里go()方法的执行代码, 如下:
| //background.cpp 线程方式运行下面的jobBody方法 BackgroundJob& BackgroundJob::go() { boost::thread t( boost::bind( &BackgroundJob::jobBody , this, _status ) ); return *this; } ////background.cpp. Background object can be only be destroyed after jobBody() ran void BackgroundJob::jobBody( boost::shared_ptr status ) { …. const string threadName = name(); if( ! threadName.empty() ) setThreadName( threadName.c_str() ); try { run();//到这里,mongos开始执行子类balancer中的run方法 } …. if( status->deleteSelf ) delete this; } |
上面代码最终会将执行流程转到balancer类的run()方法,如下
| void Balancer::run() { /* this is the body of a BackgroundJob so if we throw here we’re basically ending the balancer thread prematurely */ while ( ! inShutdown() ) { if ( ! _init() ) {//检查balancer是否链到config server和其它shard上 log() << “will retry to initialize balancer in one minute” << endl; sleepsecs( 60 ); continue; } break; } //构造链接串信息 ConnectionString config = configServer.getConnectionString(); //声明分布式锁 DistributedLock balanceLock( config , “balancer” ); while ( ! inShutdown() ) {//一直循环直到程序中断或关闭 try { // 判断chunk均衡功能是否有效 if ( ! grid.shouldBalance() ) { log(1) << “skipping balancing round because balancing is disabled” << endl; sleepsecs( 30 ); continue; } //从链接池中获取一个链接对象,如无链接则直接创建。更多内容详见connpool.cpp文件的 //DBClientBase* DBConnectionPool::get(const string& host) 方法. ScopedDbConnection conn( config ); _ping( conn.conn() );//标识链到config server的balancer为活动(live)状态 if ( ! _checkOIDs() ) { uassert( 13258 , “oids broken after resetting!” , _checkOIDs() ); } //重载Shard集合信息(shard 状态) Shard::reloadShardInfo(); //声明balance锁对象balanceLock dist_lock_try lk( &balanceLock , “doing balance round” ); if ( ! lk.got() ) { log(1) << “skipping balancing round because another balancer is active” << endl; conn.done(); sleepsecs( 30 ); // no need to wake up soon continue; } log(1) << “*** start balancing round” << endl; vector candidateChunks; //获取在shard集合中建议迁移的chunk信息(包含要迁移到的目标shard信息) _doBalanceRound( conn.conn() , &candidateChunks ); if ( candidateChunks.size() == 0 ) {//是否有要移动的chunk log(1) << “no need to move any chunk” << endl; } else//开始迁移并返回最终迁移数量 { _balancedLastTime = _moveChunks( &candidateChunks ); } log(1) << “*** end of balancing round” << endl; conn.done();//将conn放到链接池中(为其它后续操作使用) sleepsecs( _balancedLastTime ? 5 : 10 ); } catch ( std::exception& e ) { log() << “caught exception while doing balance: ” << e.what() << endl; // Just to match the opening statement if in log level 1 log(1) << “*** End of balancing round” << endl; sleepsecs( 30 ); // sleep a fair amount b/c of error continue; } } } |
上面方法中主要是先构造链接串,进而构造连接实例(注:这里使用了链接池的概念,我会在后续章节中专门介绍其实现机制)。之后刷新sharding中的相关信息(确保其有效性),之后调用_doBalanceRound()方法来收集可能要迁移的chunk(s)信息并最终完成迁移(使用_moveChunks方法)。
下面我们就着重看一下这两个方法的具体实现.
首先是_doBalanceRound方法:
| //balance.cpp void Balancer::_doBalanceRound( DBClientBase& conn, vector* candidateChunks ) { assert( candidateChunks ); // 1. 通过查询ShardsNS::collections来检查是否有可用sharded集合来均衡chunk auto_ptr cursor = conn.query( ShardNS::collection , BSONObj() ); vector< string > collections; while ( cursor->more() ) { BSONObj col = cursor->next(); // sharded collections will have a shard “key”. if ( ! col[“key”].eoo() ) collections.push_back( col[“_id”].String() ); } cursor.reset(); if ( collections.empty() ) { log(1) << “no collections to balance” << endl; return; } //获取一个需要均衡的shard信息列表,表中shard信息包括maxsize, currsiez, drain, hsopsqueued vector allShards; Shard::getAllShards( allShards ); if ( allShards.size() < 2) { log(1) << “can’t balance without more active shards” << endl; return; } //获取allShards的相应状态信息交绑定到shardLimitMap相应元素中,该shardLimitMap是一个从shardId到对象(BSONObj)的映射 map< string, BSONObj > shardLimitsMap; for ( vector::const_iterator it = allShards.begin(); it != allShards.end(); ++it ) { const Shard& s = *it; ShardStatus status = s.getStatus(); //最大值 (单位:兆字节, 0为不限制) BSONObj limitsObj = BSON( ShardFields::maxSize( s.getMaxSize() ) << LimitsFields::currSize( status.mapped() ) << //当前时间状态的信息 hardFields::draining( s.isDraining() ) << //当前的shard是否正在被移除 LimitsFields::hasOpsQueued( status.hasOpsQueued() )//是否有回写的队列信息 ); shardLimitsMap[ s.getName() ] = limitsObj; } //遍历collections集合,根据均衡策略(balancing policy) ,检查是否有要迁移的chunk信息 for (vector::const_iterator it = collections.begin(); it != collections.end(); ++it ) { const string& ns = *it;//集合的名空间 map< string,vector > shardToChunksMap;//从shardId 到chunks 的映射 cursor = conn.query( ShardNS::chunk , QUERY( “ns” << ns ).sort( “min” ) ); while ( cursor->more() ) { BSONObj chunk = cursor->next(); //以chunk所属的shard为标识,获取一个chunks的集合来收集位于同一shard的chunk vector& chunks = shardToChunksMap[chunk[“shard”].String()]; chunks.push_back( chunk.getOwned() ); } cursor.reset(); if (shardToChunksMap.empty()) { log(1) << “skipping empty collection (” << ns << “)”; continue; } for ( vector::iterator i=allShards.begin(); i!=allShards.end(); ++i ) { // this just makes sure there is an entry in shardToChunksMap for every shard Shard s = *i; shardToChunksMap[s.getName()].size(); } //找出要迁移的chunk,包括源及目标(要迁移到的)chunk的起始地址 CandidateChunk* p = _policy->balance( ns , shardLimitsMap , shardToChunksMap , _balancedLastTime /*number of moved chunks in last round*/); if ( p ) candidateChunks->push_back( CandidateChunkPtr( p ) );//存到要均衡的chunk集合中 } } |
上面的_doBalanceRound方法主要构造shardLimitsMap,shardToChunksMap这两个实例对象集合(map<>类型),其中:
shardLimitsMap:用于收集shard集合中一些“起数量限制”作用的参数,如maxsize,draining,hasOpsQueued等,因为这几个参数如果超出范围或为true时,相应shard 是不可以提供迁移服务的。
shardToChunksMap:用于收集当前shard中的chunk信息,以便后面的遍历操作。
收集了这些信息之后,通过调用 _policy->balance()方法来找出可能需要迁移的chunk().
下面就看一下该均衡策略的具体实现(具体内容参见注释):
| //balacer_policy.cpp BalancerPolicy::ChunkInfo* BalancerPolicy::balance( const string& ns, const ShardToLimitsMap& shardToLimitsMap, const ShardToChunksMap& shardToChunksMap, int balancedLastTime ) { pair min(“”,numeric_limits::max()); pair max(“”,0); vector drainingShards; //遍历shard集合,找到min,max的匹配对象,以及draining的Shard信息 for (ShardToChunksIter i = shardToChunksMap.begin(); i!=shardToChunksMap.end(); ++i ) { // 遍历shard,并查看其容量或可用空间是否被耗尽 const string& shard = i->first; BSONObj shardLimits; ShardToLimitsIter it = shardToLimitsMap.find( shard ); if ( it != shardToLimitsMap.end() ) shardLimits = it->second;//获取shard的信息,包括maxsize, currsiez, drain, hsopsqueued const bool maxedOut = isSizeMaxed( shardLimits );//shard是否已满 const bool draining = isDraining( shardLimits );//shard是否移除 const bool opsQueued = hasOpsQueued( shardLimits );//shard是否有写回队列 //是否合适接收chunk,满足下面三个条件之一,则视为不合适 // + maxed out shards // + draining shards // + shards with operations queued for writeback const unsigned size = i->second.size();//获取当前shard里的chunk数 if ( ! maxedOut && ! draining && ! opsQueued ) { if ( size < min.second ) {//如果当前shard中chunk数与min比较,找出最小size的shard min = make_pair( shard , size ); } } // 检查shard 是否应该迁移(chunk donor) // Draining shards 比 overloaded shards优先级低 if ( size > max.second ) { max = make_pair( shard , size );//找出最大size的shard } if ( draining && (size > 0)) { drainingShards.push_back( shard ); } } // 如果chunk没有合适的shard接收, 意味着上面循环中都是类以draining等情况 if ( min.second == numeric_limits::max() ) { log() << “no availalable shards to take chunks” << endl; return NULL; } log(1) << “collection : ” << ns << endl; log(1) << “donor : ” << max.second << ” chunks on ” << max.first << endl; log(1) << “receiver : ” << min.second << ” chunks on ” << min.first << endl; if ( ! drainingShards.empty() ) { string drainingStr; joinStringDelim( drainingShards, &drainingStr, ‘,’ );//用逗号将drainingShards连接起来 log(1) << “draining : ” << ! drainingShards.empty() << “(” << drainingShards.size() << “)” << endl; } // 通过优先级解决不均衡问题. const int imbalance = max.second – min.second;//找出shard中最不均衡的size的差距 const int threshold = balancedLastTime ? 2 : 8; string from, to; if ( imbalance >= threshold /*临界点*/) { from = max.first;//将shard中chunk最多的作为源 to = min.first;//将shard中chunk最小的作为要迁移的目的地 } else if ( ! drainingShards.empty() ) { //对于那些draining的shard,随机取出其中一个 from = drainingShards[ rand() % drainingShards.size() ]; to = min.first; } else { // 如已均衡,则返回 return NULL; } //找出要迁移的chunk集合的起始位置 const vector& chunksFrom = shardToChunksMap.find( from )->second; const vector& chunksTo = shardToChunksMap.find( to )->second;//找出要迁移到的chunk集合目标位置 BSONObj chunkToMove = pickChunk( chunksFrom , chunksTo );//最终选出(校正)要迁移的chunk的起始位置 log() << “chose [” << from << “] to [” << to << “] ” << chunkToMove << endl; //返回上面balaner的操作结果来执行后续的移动chunk操作 return new ChunkInfo( ns, to, from, chunkToMove ); } |
上面方法通过计算各个shard中的当前chunk数量来推算出那个shard相对较空,并将其放到to(目标shard),之后对可能要迁移的chunk进行校验,这里使用了pickChunk()方法,该方法具体实现如下:
| //balancer_policy.cpp //找出需要被迁移的chunk, 这里要考虑to端可能比from端chunks更多的情况 BSONObj BalancerPolicy::pickChunk( const vector& from, const vector& to ) { // It is possible for a donor (‘from’) shard to have less chunks than a recevier one (‘to’) // if the donor is in draining mode. if ( to.size() == 0 )//如果目标位置为空,表示可以将from中数据全部迁移过去 return from[0]; /**wo=’well ordered’. fields must be in same order in each object. Ordering is with respect to the signs of the elements and allows ascending / descending key mixing. @return <0 if l0 if l>r */ //如果要迁移的chunk中最小值与目标位置的最大值相同,表示可以将from中数据全部迁移过去 if ( from[0][“min”].Obj().woCompare( to[to.size()-1][“max”].Obj() , BSONObj() , false ) == 0 ) return from[0]; //如果要迁移的chunk中最大值与目标位置的最小值相同,表示可以将from中最后一个chunk迁移过去 if ( from[from.size()-1][“max”].Obj().woCompare( to[0][“min”].Obj() , BSONObj() , false ) == 0 ) return from[from.size()-1]; return from[0]; } |
完成了校验之后,得到的就是真正要迁移的chunk的启始地址,之后就可以进行迁移了。到这里,我们还要将执行流程跳回到Balancer::run()方法里,看一下最终完成迁移工作的方法movechunk()的实现流程:
| //balance.cpp文件 int Balancer::_moveChunks( const vector* candidateChunks ) { //最终迁移的chunk数 int movedCount = 0; //遍历要迁移chunks并逐一开始迁移 for ( vector::const_iterator it = candidateChunks->begin(); it != candidateChunks->end(); ++it ) { const CandidateChunk& chunkInfo = *it->get(); //获取当前chunk要使用的db配置信息 DBConfigPtr cfg = grid.getDBConfig( chunkInfo.ns ); assert( cfg ); //声明ChunkManager使用它来 ChunkManagerPtr cm = cfg->getChunkManager( chunkInfo.ns ); assert( cm ); //获取要迁移的chunk起始地址 const BSONObj& chunkToMove = chunkInfo.chunk; ChunkPtr c = cm->findChunk( chunkToMove[“min”].Obj() ); //下面判断执行两次,防止执行split之后,系统在reload 情况下chunk可能出现min,max不一致情况 if ( c->getMin().woCompare( chunkToMove[“min”].Obj() ) || c->getMax().woCompare( chunkToMove[“max”].Obj() ) ) { // 这里主要防止别处执行 split 操作造成负作用 cm = cfg->getChunkManager( chunkInfo.ns , true /* reload */); assert( cm ); c = cm->findChunk( chunkToMove[“min”].Obj() ); if ( c->getMin().woCompare( chunkToMove[“min”].Obj() ) || c->getMax().woCompare( chunkToMove[“max”].Obj() ) ) { log() << “chunk mismatch after reload, ignoring will retry issue cm: ” << c->getMin() << ” min: ” << chunkToMove[“min”].Obj() << endl; continue; } } BSONObj res; //将chunk, 从当前的shard ,移动到指定的shard,并累加迁移数量 if ( c->moveAndCommit( Shard::make( chunkInfo.to ) , Chunk::MaxChunkSize , res ) ) { movedCount++; continue; } //如迁移不成功,记入日志 // the move requires acquiring the collection metadata’s lock, which can fail log() << “balacer move failed: ” << res << ” from: ” << chunkInfo.from << ” to: ” << chunkInfo.to << ” chunk: ” << chunkToMove << endl; //chunk是否达到允许移动的最大尺寸,如果是,则对当前shard执行split操作 if ( res[“chunkTooBig”].trueValue() ) { // reload just to be safe cm = cfg->getChunkManager( chunkInfo.ns ); assert( cm ); c = cm->findChunk( chunkToMove[“min”].Obj() ); log() << “forcing a split because migrate failed for size reasons” << endl; res = BSONObj(); //对当前的shards进行分割(获取适合的分割点),该方法有些复杂,我会抽时间写文章介绍 c->singleSplit( true , res ); log() << “forced split results: ” << res << endl; // TODO: if the split fails, mark as jumbo SERVER-2571 } } return movedCount; } |
上面代码就是依次遍历要迁移的chunk,分别根据其ns信息获取相应的ChunkManager(该类主要执行chunk的管理,比如CRUD等),之后就通过该ChunkManager找出当前chunk中最小的值(min:参见chunk.h文件,我这里把min,max理解为当前chunk中最小和最大记录对象信息)chunk信息,并开始迁移。
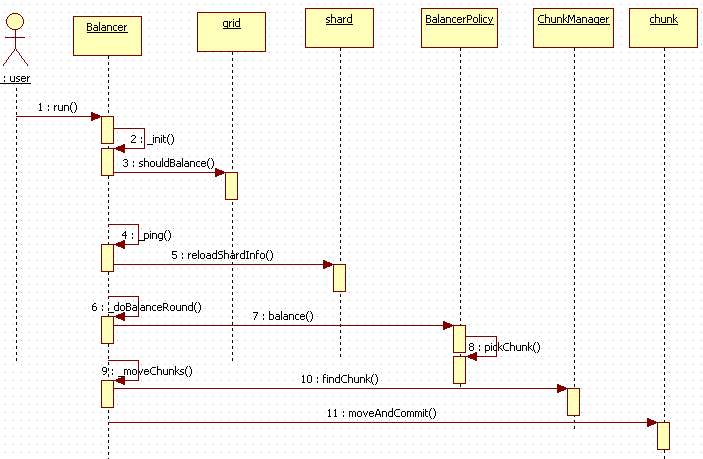
按照惯例,这里还是用一个时序列来大体回顾一下balancer的执行流程,如下:
我们一直都在努力坚持原创.......请不要一声不吭,就悄悄拿走。
我原创,你原创,我们的内容世界才会更加精彩!
【所有原创内容版权均属TechTarget,欢迎大家转发分享。但未经授权,严禁任何媒体(平面媒体、网络媒体、自媒体等)以及微信公众号复制、转载、摘编或以其他方式进行使用。】
微信公众号
TechTarget
官方微博
TechTarget中国
相关推荐
-
MongoDB与Cassandra数据库对比
MongoDB和Cassandra都属于NoSQL数据库系列,它们也恰好都是开源,但是,它们的相似之处仅此而已 […]
-
OpenWorld18大会:Ellison宣布数据库的搜寻和破坏任务
在旧金山举行的甲骨文OpenWorld 2018大会中,甲骨文首席技术官(CTO)兼创始人Larry Elli […]
-
eHarmony公司利用Redis NoSQL数据库进行热存储
虽然关系型数据库不会消失,但关系型数据库管理系统有时仅在会话管理、推荐引擎和模式匹配等关键Web应用程序中担当 […]
-
ObjectRocket着力发展Azure MongoDB服务
MongoDB吸引了微软公司的注意力,微软公司计划针对运行于该公司2017年发布的Azure Cosmos D […]
