在上文中介绍了主从(master-slave)模式下的一些基本概念及master的执行流程。今天接着介绍一下从(slave)结点是如何发起请求,并通过请求获取的oplog信息来构造本地数据的。
不过开始今天的正文前,需要介绍一下mongodb在slave结点上进行数据同步时的一个大致流程:
1.当一个从结点启动时,它会对主结点进行一次彻底同步。从结点将复制主结点中的每一个文档(操作量大且耗时)。当初始化的同步完成后,从结点将查询主结点的oplog并且执行这些操作来保持数据的更新。
2.如从结点上的操作落后主结点太多,从结点处于out-of-sync状态。该状态表示从结点不能通过执行同步操作使本地数据赶上主结点数据,因为主结点中的每一个操作都太新了。造成这种情况的原因包括结点宕机或者忙于处理读请求(尽管mongodb支持读操作的负载均衡)。如果同步的时间(戳)超出了oplog(滚动)的时间(戳),它将重新开始一次彻底的同步(通过执行resync操作)。
3.当一个从结点处于out-of- sync状态时,复制将被挂起,从结点需要从主结点进行重新同步。resync流程可以手动执行,即在从结点的admin数据库上运行命令 {“resync”:1}, 或者自动执行:在启动从结点时使用 –autoresync选项。因为resync是非常操作量大且耗时,最好通过设置一个足够大的oplogSize来避免resync(默认的 oplog大小是空闲磁盘大小的5%)。
为了验证上面的流程,下面我们就来看一下slave的执行流程。这里为了便于调试,对环境配置如下:
1.master db ip-> 10.0.4.210
启动命令行:d:mongod>bin>mongod –dbpath=d:mongodbdb –master –oplogSize 64
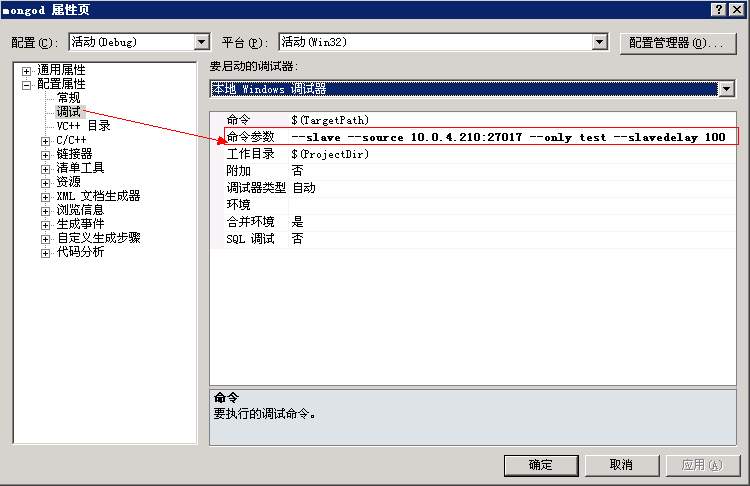
2.在vs中做如下设置(mongod项目属性窗口):
–slave –source 10.0.4.210:27017 –only test –slavedelay 100
因为mongod的主入口函数在db.cpp中,我们可以通过下面方法的调用流程找到slave的蛛丝马迹:
db.cpp–>
main(int argc, char* argv[]) //加载启动参数如–slave,–slavedelay并绑定到replSettings对象
void initAndListen(int listenPort, const char *appserverLoc = NULL)
void _initAndListen(int listenPort, const char *appserverLoc = NULL)
listen(int port)
当执行到listen()方法后(如下):
void listen(int port) {
//testTheDb();
log() << “waiting for connections on port ” << port << endl;
OurListener l(cmdLine.bind_ip, port);
l.setAsTimeTracker();
//启动复制
startReplication();
if ( !noHttpInterface )
boost::thread web( boost::bind(&webServerThread, new RestAdminAccess() /* takes ownership */));
…..
}
mongodb会紧跟着执行repl.cpp文件中的startReplication()方法,如下:
//repl.cpp
void startReplication() {
/* if we are going to be a replica set, we aren’t doing other forms of replication. */
if( !cmdLine._replSet.empty() ) {
//如果使用分布集群,则不允许带slave或master选项
if( replSettings.slave || replSettings.master || replPair ) {
log() << “***” << endl;
log() << “ERROR: can’t use –slave or –master replication options with –replSet” << endl;
log() << “***” << endl;
}
//绑定函数,oplog.cpp ->_logOpRS(), 用于处理replset类型的oplog操作
newRepl();
return;
}
//绑定函数,oplog.cpp ->_logOpOld(), 用于处理master-slave类型的oplog操作
oldRepl();
/* this was just to see if anything locks for longer than it should — we need to be careful
not to be locked when trying to connect() or query() the other side.
*/
//boost::thread tempt(tempThread);
//当设置参数不正确时(非slave,master且不是replPair)
if( !replSettings.slave && !replSettings.master && !replPair )
return;
{
dblock lk;
cc().getAuthenticationInfo()->authorize(“admin”);
pairSync->init();
}
//如果是slave,则开启相关访问(master server)线程
if ( replSettings.slave || replPair ) {
if ( replSettings.slave ) {
assert( replSettings.slave == SimpleSlave );
log(1) << “slave=true” << endl;
}
else
replSettings.slave = ReplPairSlave;
//构造并启动线程方法replSlaveThread
boost::thread repl_thread(replSlaveThread);
}
//如果是master,则构造并启动线程方法replMasterThread
if ( replSettings.master || replPair ) {
if ( replSettings.master )
log(1) << “master=true” << endl;
replSettings.master = true;
createOplog();//构造oplog集合“local.oplog.$main”
boost::thread t(replMasterThread);
}
// don’t allow writes until we’ve set up from log
while( replSettings.fastsync )
sleepmillis( 50 );
}
上面方法在完成必要的参数分析检查之后,就会根据slave的配置信息来构造启动线程方法replSlaveThread,如下:
//repl.cpp
void replSlaveThread() {
sleepsecs(1);
Client::initThread(“replslave”);
cc().iAmSyncThread();
{
dblock lk;
//获取认证信息(mongodb支持使用安全认证不管哪种replicate方式,
//只要在master/slave中创建一个能为各个database认识的用户名/密码即可)
cc().getAuthenticationInfo()->authorize(“admin”);
……
}
while ( 1 ) {
try {
//repl主函数
replMain();
if ( debug_stop_repl )
break;
sleepsecs(5);//休眠5秒
}
catch ( AssertionException& ) {
ReplInfo r(“Assertion in replSlaveThread(): sleeping 5 minutes before retry”);
problem() << “Assertion in replSlaveThread(): sleeping 5 minutes before retry” << endl;
sleepsecs(300);
}
}
}
上面方法中有mongodb进行认证的逻辑,之后就会用一个while(1)来循环执行(注:每5秒执行一次)replMain()方法,如下:
//repl.cpp
void replMain() {
ReplSource::SourceVector sources;
while ( 1 ) {
int s = 0;
{
dblock lk;
//复制失败
if ( replAllDead ) {//该标识符会在同步出现异常如(out of sync)时为true
//autoresync:自动地重新执行完整的同步,如果这个从结点脱离了与主结点的同步。
if ( !replSettings.autoresync || !ReplSource::throttledForceResyncDead( “auto” ) )
break;
}
// i.e., there is only one sync thread running.
// we will want to change/fix this.
assert( syncing == 0 );
syncing++;
}
try {
int nApplied = 0;
//repl主函数
s = _replMain(sources, nApplied);
if( s == 1 ) {
if( nApplied == 0 ) s = 2;
else if( nApplied > 100 ) {
// sleep very little – just enought that we aren’t truly hammering master
sleepmillis(75);
s = 0;
}
}
}
catch (…) {
out() << “caught exception in _replMain” << endl;
s = 4;
}
……
}
上面代码又是一个while(1)循环,它会判断当前slave是否处于“out of sync”状态,如果是,但未开启autoresync时,则复制将被挂起。否则会执行_replMain方法来进行同步,如下:
//repl.cpp
int _replMain(ReplSource::SourceVector& sources, int& nApplied) {
{
ReplInfo r(“replMain load sources”);
dblock lk;
ReplSource::loadAll(sources);//绑定相应的master sources,以便后面遍历同步
/*fastsync: 从主结点的快照中启动一个从结点。与完整的同步相比,
这个选项允许一个从结点更快地启动,如果它的数据目录已经使用主结点的快照进行初始化。*/
replSettings.fastsync = false; // 初始重置时需要该参数
}
…..
int sleepAdvice = 1;
for ( ReplSource::SourceVector::iterator i = sources.begin(); i != sources.end(); i++ ) {
ReplSource *s = i->get();
int res = -1;
try {
res = s->sync(nApplied);
//是否有其它要同步的数据库
bool moreToSync = s->haveMoreDbsToSync();
if( res < 0 ) {
sleepAdvice = 3;
}
else if( moreToSync ) {
sleepAdvice = 0;
}
else if ( s->sleepAdvice() ) {
sleepAdvice = s->sleepAdvice();
}
else
sleepAdvice = res;
if ( res >= 0 && !moreToSync /*&& !s->syncedTo.isNull()*/ ) {
pairSync->setInitialSyncCompletedLocking();
}
}
……
}
return sleepAdvice;
}
上面的_replMain()方法首先会从“local.sources”数据集中获取主(master)节点的信息。这里解释一下,mongod从结点在启动时会将启动参数(–source)中的信息保存到”local.sources”数据集中,并通过此函数(loadAll())中加载到一个集合对象中。这里我们看一下其加载代码,如下:
/* slave: pull some data from the master’s oplog
note: not yet in db mutex at this point.
@return -1 error
0 ok, don’t sleep
1 ok, sleep
*/
//repl.cpp
void ReplSource::loadAll(SourceVector &v) {
Client::Context ctx(“local.sources”);
SourceVector old = v;
v.clear();
……
//遍历local.sources,并将其中的replsource绑定到SourceVector中
shared_ptr<Cursor> c = findTableScan(“local.sources”, BSONObj());
while ( c->ok() ) {
ReplSource tmp(c->current());
if ( replPair && tmp.hostName == replPair->remote && tmp.sourceName() == “main” ) {
gotPairWith = true;
tmp.paired = true;
if ( replacePeer ) {
// peer was replaced — start back at the beginning.
tmp.syncedTo = OpTime();
tmp.replacing = true;
}
}
if ( ( !replPair && tmp.syncedTo.isNull() ) ||
( replPair && replSettings.fastsync ) ) {
DBDirectClient c;
//主服务器进程创建的local.oplog.$main数据集,即”transaction log”,以记录从服务器需要的操作队列信息。
//这里用于获取同步时的时间戳”syncedTo”
if ( c.exists( “local.oplog.$main” ) ) {
BSONObj op = c.findOne( “local.oplog.$main”, QUERY( “op” << NE << “n” ).sort( BSON( “$natural” << -1 ) ) );
if ( !op.isEmpty() ) {
tmp.syncedTo = op[ “ts” ].date();
tmp._lastSavedLocalTs = op[ “ts” ].date();
}
}
}
//将source数据绑定到v中以引用方式(&v)返回给上一级函数调用
addSourceToList(v, tmp, old);
c->advance();
}
……
}
完成了source的加载之后,就可以开始对source进行同步了,即如下代码:
int ReplSource::sync(int& nApplied) {
_sleepAdviceTime = 0;
ReplInfo r(“sync”);
if ( !cmdLine.quiet ) {
Nullstream& l = log();
l << “repl: from “;
if( sourceName() != “main” ) {
l << “source:” << sourceName() << ‘ ‘;
}
l << “host:” << hostName << endl;
}
nClonedThisPass = 0;
// 对于localhost这类本机地址,则不能同步
//FIXME Handle cases where this db isn’t on default port, or default port is spec’d in hostName.
if ( (string(“localhost”) == hostName || string(“127.0.0.1”) == hostName) && cmdLine.port == CmdLine::DefaultDBPort ) {
log() << “repl: can’t sync from self (localhost). sources configuration may be wrong.” << endl;
sleepsecs(5);
return -1;
}
//oplogReader链接时出现异常
if ( !oplogReader.connect(hostName) ) {
log(4) << “repl: can’t connect to sync source” << endl;
if ( replPair && paired ) {
assert( startsWith(hostName.c_str(), replPair->remoteHost.c_str()) );
replPair->arbitrate();//paired模式下同级结点进行仲裁
}
return -1;
}
if ( paired ) {
int remote = replPair->negotiate(oplogReader.conn(), “direct”);
int nMasters = ( remote == ReplPair::State_Master ) + ( replPair->state == ReplPair::State_Master );
//主库不为1时,则异常
if ( getInitialSyncCompleted() && nMasters != 1 ) {
log() << ( nMasters == 0 ? “no master” : “two masters” ) << “, deferring oplog pull” << endl;
return 1;
}
}
……
return sync_pullOpLog(nApplied);//根据oplog日志进行同步
}
上面方法先进行一些异常判断,比如source为localhost地址,以及无法链接(oplogReader.connect)等情况。之后,调用sync_pullOpLog方法,从master上获取oplog来同步数据信息,如下:
//repl.cpp 获取主库的oplog数据
int ReplSource::sync_pullOpLog(int& nApplied) {
int okResultCode = 1;
//获取主库中oplog的名空间信息
string ns = string(“local.oplog.$”) + sourceName();
log(2) << “repl: sync_pullOpLog ” << ns << ” syncedTo:” << syncedTo.toStringLong() << ‘n’;
bool tailing = true;
oplogReader.tailCheck();
if ( replPair && replPair->state == ReplPair::State_Master ) {
dblock lk;
idTracker.reset();
}
OpTime localLogTail = _lastSavedLocalTs;
//是否初始化
bool initial = syncedTo.isNull();
//无游标支持或要初始化时
if ( !oplogReader.haveCursor() || initial ) {
if ( initial ) {
//显示数据库信息之前,获取最新(last)的 oplog日志时间戳.
syncToTailOfRemoteLog();
BSONObj info;
bool ok = oplogReader.conn()->runCommand( “admin”, BSON( “listDatabases” << 1 ), info );
massert( 10389 , “Unable to get database list”, ok );
BSONObjIterator i( info.getField( “databases” ).embeddedObject() );
while( i.moreWithEOO() ) {
BSONElement e = i.next();
if ( e.eoo() )
break;
string name = e.embeddedObject().getField( “name” ).valuestr();
if ( !e.embeddedObject().getBoolField( “empty” ) ) {
if ( name != “local” ) {
if ( only.empty() || only == name ) {
log( 2 ) << “adding to ‘addDbNextPass’: ” << name << endl;
addDbNextPass.insert( name );
}
}
}
}
dblock lk;
save();
}
//本次同步的日志时间戳(gte:大于或等于)
BSONObjBuilder q;
q.appendDate(“$gte”, syncedTo.asDate());
BSONObjBuilder query;
query.append(“ts”, q.done());
if ( !only.empty() ) {
// note we may here skip a LOT of data table scanning, a lot of work for the master.
query.appendRegex(“ns”, string(“^”) + only); // maybe append “\.” here?
}
BSONObj queryObj = query.done();
// e.g. queryObj = { ts: { $gte: syncedTo } }
//tailingQuery查询,并绑定其相应游标信息
oplogReader.tailingQuery(ns.c_str(), queryObj);
tailing = false;
}
else {
log(2) << “repl: tailing=truen”;
}
//如果依旧无游标信息,可能链接被关闭,则尝试重置链接
if( !oplogReader.haveCursor() ) {
problem() << “repl: dbclient::query returns null (conn closed?)” << endl;
oplogReader.resetConnection();
return -1;
}
// show any deferred(延期,搁置)database creates from a previous pass
{
set<string>::iterator i = addDbNextPass.begin();
if ( i != addDbNextPass.end() ) {
BSONObjBuilder b;
b.append(“ns”, *i + ‘.’);
b.append(“op”, “db”);
BSONObj op = b.done();
//找到相应的oplog之后并使用这些oplog操作同步,方法很复杂,这里暂且略过
sync_pullOpLog_applyOperation(op, 0, false);
}
}
if ( !oplogReader.more() ) {//如没有其它oplog操作,则返回
if ( tailing ) {//已到cap collection结尾
log(2) << “repl: tailing & no new activityn”;
if( oplogReader.awaitCapable() )
okResultCode = 0; // don’t sleep
}
else {
log() << “repl: ” << ns << ” oplog is emptyn”;
}
{
dblock lk;
//最近一次保存到本地操作发生时间
OpTime nextLastSaved = nextLastSavedLocalTs();
{
dbtemprelease t;
if ( !oplogReader.more() ) {
//设置_lastSavedLocalTs
setLastSavedLocalTs( nextLastSaved );
}
}
save();
}
return okResultCode;
}
//下一次操作时间,用于绑定到syncedTo上。
//syncedTo为时间戳,保存从结点的更新时间,每次从结点需要查询新的oplog时,
//它使用“syncedTo”获得它需要执行的新的操作,或者发现它已经out-of-sync。
OpTime nextOpTime;
{
BSONObj op = oplogReader.next();
BSONElement ts = op.getField(“ts”);
if ( ts.type() != Date && ts.type() != Timestamp ) {
string err = op.getStringField(“$err”);
//如获取master oplog时出现error
if ( !err.empty() ) {
// 13051 is “tailable cursor requested on non capped collection”
if (op.getIntField(“code”) == 13051) {
problem() << “trying to slave off of a non-master” << ‘n’;
massert( 13344 , “trying to slave off of a non-master”, false );
}
else {
problem() << “repl: $err reading remote oplog: ” + err << ‘n’;
massert( 10390 , “got $err reading remote oplog”, false );
}
}
else {
problem() << “repl: bad object read from remote oplog: ” << op.toString() << ‘n’;
massert( 10391 , “repl: bad object read from remote oplog”, false);
}
}
if ( replPair && replPair->state == ReplPair::State_Master ) {
OpTime next( ts.date() );
if ( !tailing && !initial && next != syncedTo ) {
//强制slave 重新同步
log() << “remote slave log filled, forcing slave resync” << endl;
resetSlave();
return 1;
}
dblock lk;
updateSetsWithLocalOps( localLogTail, true );
}
nextOpTime = OpTime( ts.date() );
log(2) << “repl: first op time received: ” << nextOpTime.toString() << ‘n’;
if ( initial ) {
log(1) << “repl: initial runn”;
}
if( tailing ) {
//当出现旧数据被新oplog覆盖的情况时
if( !( syncedTo < nextOpTime ) ) {
log() << “repl ASSERTION failed : syncedTo < nextOpTime” << endl;
log() << “repl syncTo: ” << syncedTo.toStringLong() << endl;
log() << “repl nextOpTime: ” << nextOpTime.toStringLong() << endl;
assert(false);
}
oplogReader.putBack( op ); // op will be processed in the loop below
nextOpTime = OpTime(); // will reread the op below
}
//如本次同步时间与下一次操作时间不相同,意味着从结点上的操作落后主结点太多,从结点处于out-of-sync状态。
//一个out-of-sync的从结点不能通过执行操作赶上主结点,因为主结点中的每一个操作都太新了。这可能是因为从
//结点挂了或者忙于处理读请求。如果同步的时间超出了oplog滚动的时间,它将重新开始一次彻底的同步。
else if ( nextOpTime != syncedTo ) { // didn’t get what we queried for – error
Nullstream& l = log();
l << “repl: nextOpTime ” << nextOpTime.toStringLong() << ‘ ‘;
if ( nextOpTime < syncedTo )
l << “<??”;
else
l << “>”;
l << ” syncedTo ” << syncedTo.toStringLong() << ‘n’;
log() << “repl: time diff: ” << (nextOpTime.getSecs() – syncedTo.getSecs()) << “secn”;
log() << “repl: tailing: ” << tailing << ‘n’;
log() << “repl: data too stale, halting replication” << endl;
replInfo = replAllDead = “data too stale halted replication”;
assert( syncedTo < nextOpTime );
throw SyncException();
}
else {
/* t == syncedTo, so the first op was applied previously or it is the first op of initial query and need not be applied. */
}
}
//将获取到的oplog操作信息应用到“从结点(slave)”上
//apply operations
{
int n = 0;
time_t saveLast = time(0);
while ( 1 ) {
bool moreInitialSyncsPending = !addDbNextPass.empty() && n; // we need “&& n” to assure we actually process at least one op to get a sync point recorded in the first place.
if ( moreInitialSyncsPending || !oplogReader.more() ) {
dblock lk;
OpTime nextLastSaved = nextLastSavedLocalTs();
{
dbtemprelease t;
if ( !moreInitialSyncsPending && oplogReader.more() ) {
if ( getInitialSyncCompleted() ) { // if initial sync hasn’t completed, break out of loop so we can set to completed or clone more dbs
continue;
}
}
else {
setLastSavedLocalTs( nextLastSaved );
}
}
if( oplogReader.awaitCapable() && tailing )
okResultCode = 0; // don’t sleep
//syncedTo设置时间戳,保存从结点的更新时间,用于下次从结点需要查询新的oplog时,
//它使用“syncedTo”获得它需要的新的oplog,或者用于发现它已经out-of-sync。
syncedTo = nextOpTime;
save(); // note how far we are synced up to now
log() << “repl: applied ” << n << ” operations” << endl;
nApplied = n;
log() << “repl: end sync_pullOpLog syncedTo: ” << syncedTo.toStringLong() << endl;
break;
}
else {
}
…..
BSONObj op = oplogReader.next();
unsigned b = replApplyBatchSize;
bool justOne = b == 1;
scoped_ptr<writelock> lk( justOne ? 0 : new writelock() );
while( 1 ) {
BSONElement ts = op.getField(“ts”);
//类型异常判断
if( !( ts.type() == Date || ts.type() == Timestamp ) ) {
log() << “sync error: problem querying remote oplog record” << endl;
log() << “op: ” << op.toString() << endl;
log() << “halting replication” << endl;
replInfo = replAllDead = “sync error: no ts found querying remote oplog record”;
throw SyncException();
}
OpTime last = nextOpTime;
nextOpTime = OpTime( ts.date() );
//当上次操作时间比下一次操作时间要更晚,表示cap collection发生了前部数据被overwrite的情况
//这时系统会执行resync,相关问题参见:
//http://www.snailinaturtleneck.com/blog/2010/10/14/getting-to-know-your-oplog/
if ( !( last < nextOpTime ) ) {
log() << “sync error: last applied optime at slave >= nextOpTime from master” << endl;
log() << ” last: ” << last.toStringLong() << endl;
log() << ” nextOpTime: ” << nextOpTime.toStringLong() << endl;
log() << ” halting replication” << endl;
replInfo = replAllDead = “sync error last >= nextOpTime”;
uassert( 10123 , “replication error last applied optime at slave >= nextOpTime from master”, false);
}
//在从结点中指定一个从主结点中申请操作的延迟时间(单位是秒)。
//这使得构造一个delayed slaves变得容易。假如用户意外地删了重要的文档或者插入了坏的数据,这些操作都会复制到所有的从结点中。依靠delaying应用程序的操作,你将有可能从错误的操作中恢复。
if ( replSettings.slavedelay && ( unsigned( time( 0 ) ) < nextOpTime.getSecs() + replSettings.slavedelay ) ) {
assert( justOne );
oplogReader.putBack( op );
//设置sleep时间
_sleepAdviceTime = nextOpTime.getSecs() + replSettings.slavedelay + 1;
dblock lk;
if ( n > 0 ) {
//syncedTo设置时间戳,保存从结点的更新时间,用于下次从结点需要查询新的oplog时,
//它使用“syncedTo”获得它需要的新的oplog,或者用于发现它已经out-of-sync。
syncedTo = last;
save();
}
log() << “repl: applied ” << n << ” operations” << endl;
log() << “repl: syncedTo: ” << syncedTo.toStringLong() << endl;
log() << “waiting until: ” << _sleepAdviceTime << ” to continue” << endl;
return okResultCode;
}
sync_pullOpLog_applyOperation(op, &localLogTail, !justOne);
n++;
if( –b == 0 )
break;
// if to here, we are doing mulpile applications in a singel write lock acquisition
if( !oplogReader.moreInCurrentBatch() ) {
// break if no more in batch so we release lock while reading from the master
break;
}
op = oplogReader.next();
getDur().commitIfNeeded();
}
}
}
return okResultCode;
}
上面方法代码比较长,首先它会初始要链接的master的oplog名空间信息,之后尝试链接到master上以获取相应的cursor id信息。该cursor id用于标识当前slave访问master时所使用的cursor(因为master中的oplog cursor会在返回oplog信息时不关闭,它支持下次slave链接使用该cursor时从相应的pos位置继续获取。这块内容可以参见这篇文章 Mongodb源码分析–Replication之主从模式–Master).
如果cursorid正常,则使用oplogReader对象来获取相应的oplog信息(注:oplogReader为mongodb为了查询oplog而声明的一个类,详情参见其源码文件oplogreader.h)
除此以外,上面方法还会设置本地的syncedTo来记录下次同步时使用的时间戳。同时根据本地保存的时间戳与oplogReader所返回的 master oplog信息中的ts进行比较,以判断是否出现out of sync的情况,以进而执行resync操作。有关这类逻辑说明参见上面的代码注释即可。
当获取的master oplog符合(本地时间戳)要求时,则将oplog对象进行分解,以进而将其中的数据对象保存到本地并执行持久化操作(上面代码段:getDur().commitIfNeeded())。这里要说明的是,将oplog进行分解时执行的逻辑通过 sync_pullOpLog_applyOperation方法中执行,因为这里牵扯到oplog的数据结构,由于篇幅所限,这部分内容我会在后面章节中进行说明,我们只要知道在分解结束后,最终调用如下方法将数据放到本机上:
//repl.cpp
void ReplSource::applyOperation(const BSONObj& op) {
//oplog.cpp
void applyOperation_inlock(const BSONObj& op , bool fromRepl ) {
OpCounters * opCounters = fromRepl ? &replOpCounters : &globalOpCounters;
if( logLevel >= 6 )
log() << “applying op: ” << op << endl;
assertInWriteLock();
OpDebug debug;
BSONObj o = op.getObjectField(“o”);//实际操作的document
const char *ns = op.getStringField(“ns”);
// operation type — see logOp() comments for types
const char *opType = op.getStringField(“op”);
if ( *opType == ‘i’ ) {//插入
opCounters->gotInsert();
const char *p = strchr(ns, ‘.’);
if ( p && strcmp(p, “.system.indexes”) == 0 ) {
// updates aren’t allowed for indexes — so we will do a regular insert. if index already
// exists, that is ok.
theDataFileMgr.insert(ns, (void*) o.objdata(), o.objsize());
}
else {
// do upserts for inserts as we might get replayed more than once
BSONElement _id;
if( !o.getObjectID(_id) ) {
/* No _id. This will be very slow. */
Timer t;
updateObjects(ns, o, o, true, false, false , debug );
if( t.millis() >= 2 ) {
RARELY OCCASIONALLY log() << “warning, repl doing slow updates (no _id field) for ” << ns << endl;
}
}
else {
BSONObjBuilder b;
b.append(_id);
RARELY ensureHaveIdIndex(ns); // otherwise updates will be slow
updateObjects(ns, o, b.done(), true, false, false , debug );
}
}
}
else if ( *opType == ‘u’ ) {//更新
opCounters->gotUpdate();
RARELY ensureHaveIdIndex(ns); // otherwise updates will be super slow
updateObjects(ns, o, op.getObjectField(“o2”), /*upsert*/ op.getBoolField(“b”), /*multi*/ false, /*logop*/ false , debug );
}
else if ( *opType == ‘d’ ) {//删除
opCounters->gotDelete();
if ( opType[1] == 0 )
deleteObjects(ns, o, op.getBoolField(“b”));
else
assert( opType[1] == ‘b’ ); // “db” advertisement
}
else if ( *opType == ‘n’ ) {//无操作
// no op
}
else if ( *opType == ‘c’ ) {//command
opCounters->gotCommand();
BufBuilder bb;
BSONObjBuilder ob;
_runCommands(ns, o, bb, ob, true, 0);
}
else {
stringstream ss;
ss << “unknown opType [” << opType << “]”;
throw MsgAssertionException( 13141 , ss.str() );
}
}
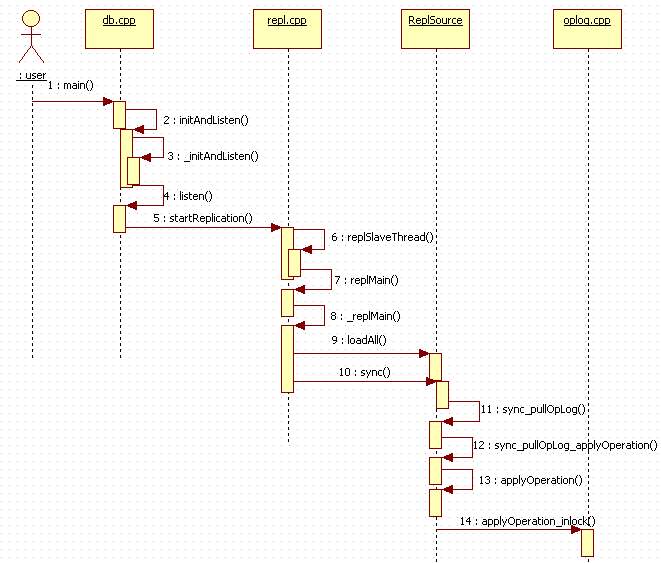
到这里,关于如何进行crud的操作,就与我之前的几篇文章的内容关联上了,大家回顾一下即可。最后用一次时序图来回顾一下slave的执行流程:
好了,今天的内容到这里就告一段落了。
我们一直都在努力坚持原创.......请不要一声不吭,就悄悄拿走。
我原创,你原创,我们的内容世界才会更加精彩!
【所有原创内容版权均属TechTarget,欢迎大家转发分享。但未经授权,严禁任何媒体(平面媒体、网络媒体、自媒体等)以及微信公众号复制、转载、摘编或以其他方式进行使用。】
微信公众号
TechTarget
官方微博
TechTarget中国
作者
相关推荐
-
MongoDB与Cassandra数据库对比
MongoDB和Cassandra都属于NoSQL数据库系列,它们也恰好都是开源,但是,它们的相似之处仅此而已 […]
-
OpenWorld18大会:Ellison宣布数据库的搜寻和破坏任务
在旧金山举行的甲骨文OpenWorld 2018大会中,甲骨文首席技术官(CTO)兼创始人Larry Elli […]
-
eHarmony公司利用Redis NoSQL数据库进行热存储
虽然关系型数据库不会消失,但关系型数据库管理系统有时仅在会话管理、推荐引擎和模式匹配等关键Web应用程序中担当 […]
-
ObjectRocket着力发展Azure MongoDB服务
MongoDB吸引了微软公司的注意力,微软公司计划针对运行于该公司2017年发布的Azure Cosmos D […]
